Grade Manager
A full-stack mobile application for academic grade management built with React Native and Spring Boot, featuring modern architecture patterns and comprehensive testing.
Planning & Technology Stack
Technology Decisions
After completing various vocational training courses, we had access to a broad range of technologies. For the backend, we learned Spring Boot, and for the frontend, we gained experience with React Native.
Since we had recently worked intensively with both technologies in our courses, we decided to continue with this stack. React Native was particularly appealing because it allows us to develop the application once and export it for all platforms.
For the data layer, we chose MariaDB, a relational database that we had also used in our training courses.
Project Language Distribution

Use Cases
User Registration
Use Case ID: 1
The user registers for the application
Procedure:
- User navigates to registration page
- User fills in name, email, and password fields
- Optional: User uploads profile picture
- If all fields are valid, send registration request
User Login
Use Case ID: 2
The user logs into the application
Procedure:
- User navigates to login page
- User fills in email and password fields
- If fields are valid and credentials exist, log user in
Add Grade
Use Case ID: 3
The user adds a new grade
Procedure:
- User navigates to grade creation page
- User fills in grade, school, subject, and weight fields
- If all fields are valid, save the grade
Edit Grade
Use Case ID: 5
The user edits an existing grade
Procedure:
- User navigates to grade editing page
- User selects the grade to edit
- User updates grade, school, subject, and weight fields
- If all fields are valid, update the grade
Project Management
GitHub Projects Integration
To make the implementation process of our 3-tier application as timely and enjoyable as possible, we placed great emphasis on planning. We had excellent experiences with GitHub Projects in previous projects.
Issues in our GitHub repository are graphically displayed through GitHub Projects in a Kanban board, giving us as developers a direct overview of the application's development status.
Kanban Board Overview
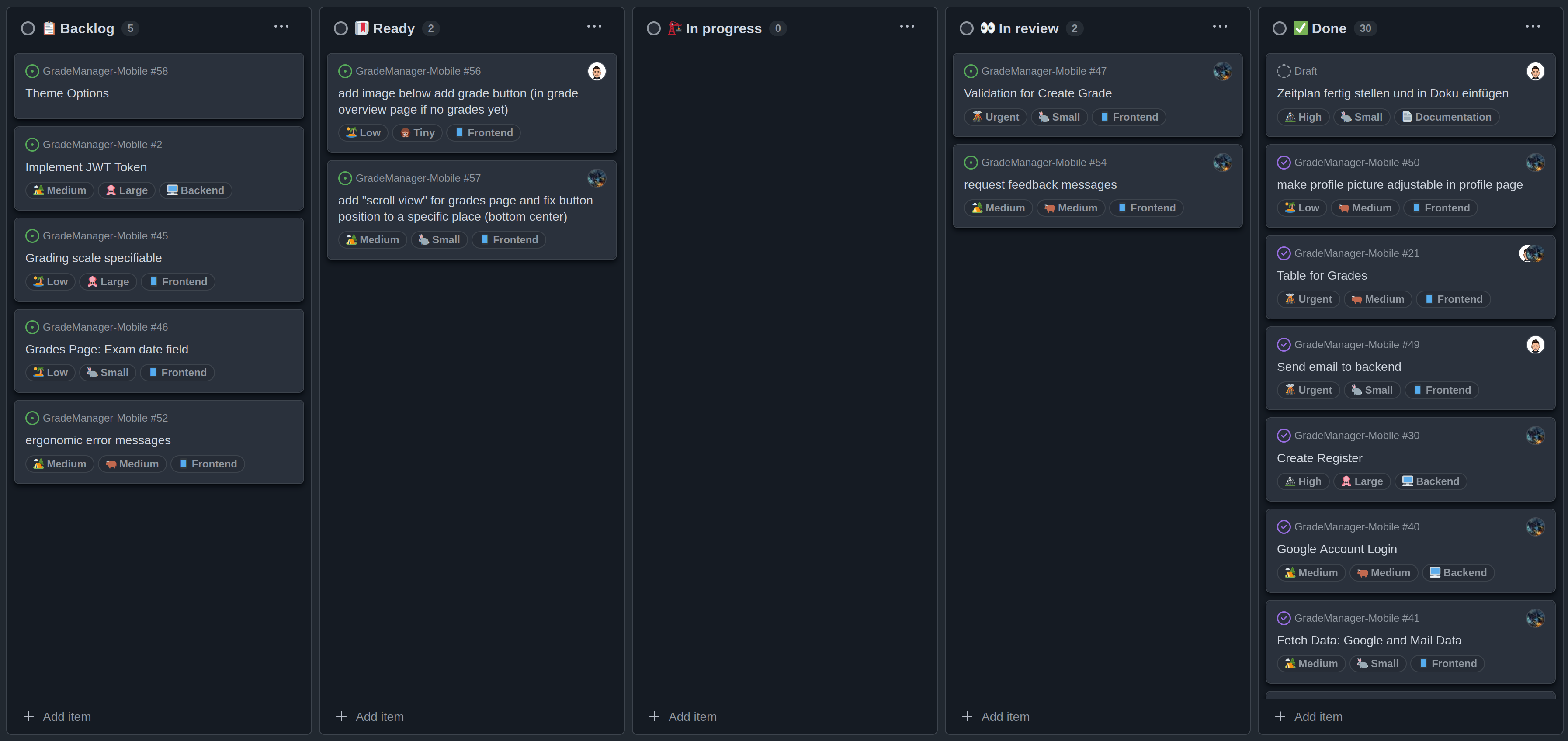
Initially, we created the most necessary tasks as issues in the Ready column and clarified who would start with which task. The biggest advantage for us developers is that everyone can work independently and assign themselves a task they're interested in. Once a task is completed, it's moved to "In review" so the other team member can review the implementation, providing opportunities for mutual learning.
Architecture & Design
Frontend Architecture
We work with the React Native framework, which allows us to compile a cross-platform app. As developers, we only need to write the code once, and it works on all platforms.
Models
In our application, classes are stored in a folder named "model". We have 2 main classes: the Grade class and the User class, containing all attributes our application needs.
Grade Model
- • id: string
- • name: string
- • grade: number
- • subject: string
- • school: string
- • user: User
User Model
- • id: string
- • email: string
- • password: string
- • name: string
- • profilePictureUrl: string
Services
Services handle processes that aren't directly related to the UI. We created 3 services:
Grade Service
Handles all grade-related information and connects with the backend. Uses JavaScript's fetch() method to send requests to our Spring Boot backend, converting objects to JSON strings.
Theme Storage Service
Responsible for local storage of theme selection. Can save, replace, and reload the currently selected theme using AsyncStorage community implementation.
User Service
Handles registration and login functionality, plus automatic login persistence. When users visit the login page, it checks for stored credentials and attempts automatic login.
Component Architecture
Atoms
Basic building blocks like input fields and text elements
Molecules
Combinations of atoms, like input fields with labels
Organisms
Collections of molecules and atoms forming complex components
Screens
Complete application pages combining all component types
Backend Architecture
We work with the Spring Framework, which simplifies backend application creation with features like easy-to-configure REST endpoints and automatic DDL generation with Hibernate.
Entities
Each database table has a corresponding entity represented by a Java class with important annotations:
@Entity (name = "grades")
@Setter
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class Grade {
@Id
private String id;
private String name;
private double grade;
private String subject;
private String school;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "user_id")
private User user;
}@Entity
Indicates that a database table should be created for this class
@Id
Marks the primary key column as unique identifier
@ManyToOne
Creates foreign key relationships between entities
Controllers
REST endpoints are created using controllers, serving as the interface between the Spring Boot application and the internet:
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/api/grades")
public class GradeController {
private final GradeService gradeService;
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public List<Grade> getGradesByUserID(@PathVariable("id") String userId) {
return gradeService.getGradesByUserID(userId);
}
@PostMapping("/persistence/addgrade")
public Grade saveGrade(@RequestBody Grade grade) throws LoginException {
return gradeService.saveGrade(grade);
}
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{id}")
public void deleteGradeByID(@PathVariable("id") String gradeId) {
gradeService.deleteGradeByID(gradeId);
}
@PutMapping("/update/{id}")
public Grade updateGradeByID(
@PathVariable("id") String gradeId,
@RequestBody Grade updatedGrade
) {
return gradeService.updateGradeByID(gradeId, updatedGrade);
}
}Services
Services process data from endpoints, handling calculations, modifications, and creation. They typically consist of an interface and corresponding implementation:
public interface GradeService {
List<Grade> getAllGrades();
Grade getGradeByID(String id);
Grade saveGrade(Grade grade);
List<Grade> getGradesByUserID(String userId);
void deleteGradeByID(String gradeId);
Grade updateGradeByID(String gradeId, Grade newGrade);
}
@Service
public class GradeServiceImpl implements GradeService {
@Autowired
private GradeRepository gradeRepository;
@Override
public Grade saveGrade(Grade grade) {
return gradeRepository.save(grade);
}
@Override
public void deleteGradeByID(String gradeId) {
gradeRepository.deleteById(gradeId);
}
}Repository
The repository is crucial for data management, providing easy database communication and serving as the interface between Java code and SQL queries:
@Repository
public interface GradeRepository extends JpaRepository<Grade, String> {
List<Grade> findByUser_Id(String id);
}The interface has minimal content because we inherit from JpaRepository, providing many predefined methods like findById() and getAll(). Spring handles the implementation internally, saving significant development time.
Design System
We followed Material Design 3 guidelines to ensure a modern and consistent user experience across the application.
Color Palette

Mockups & User Interface
Before starting development, we invested significant thought into the design and expressed our ideas through comprehensive mockups.
Authentication Screens
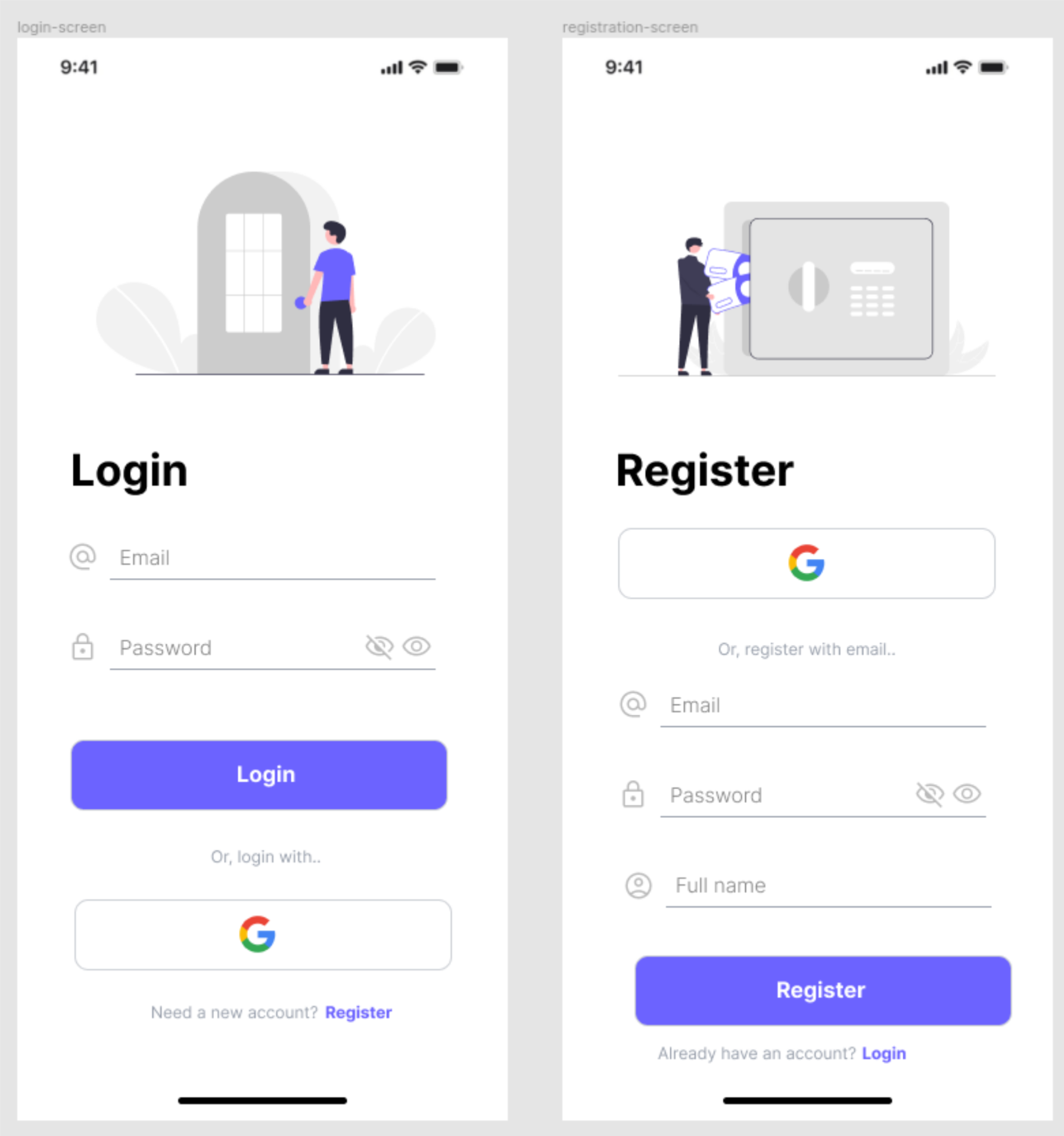
The login and registration screens are the first pages users see, making them crucial for conveying a good first impression of our design.
Profile Overview
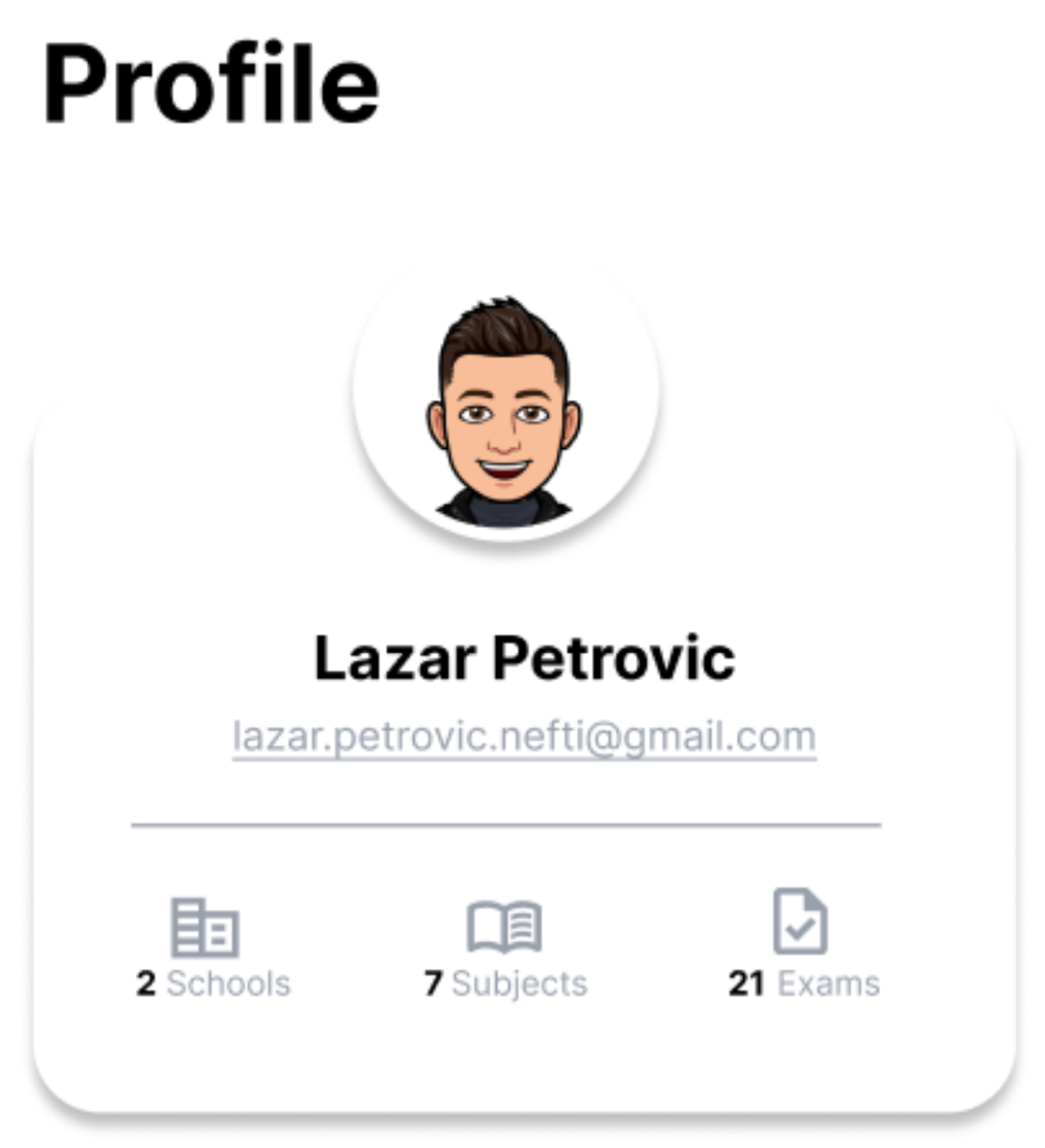
We wanted to give users a good overview of their activities in the app, showing important statistics at a glance without getting lost in various submenus.
Grade Management
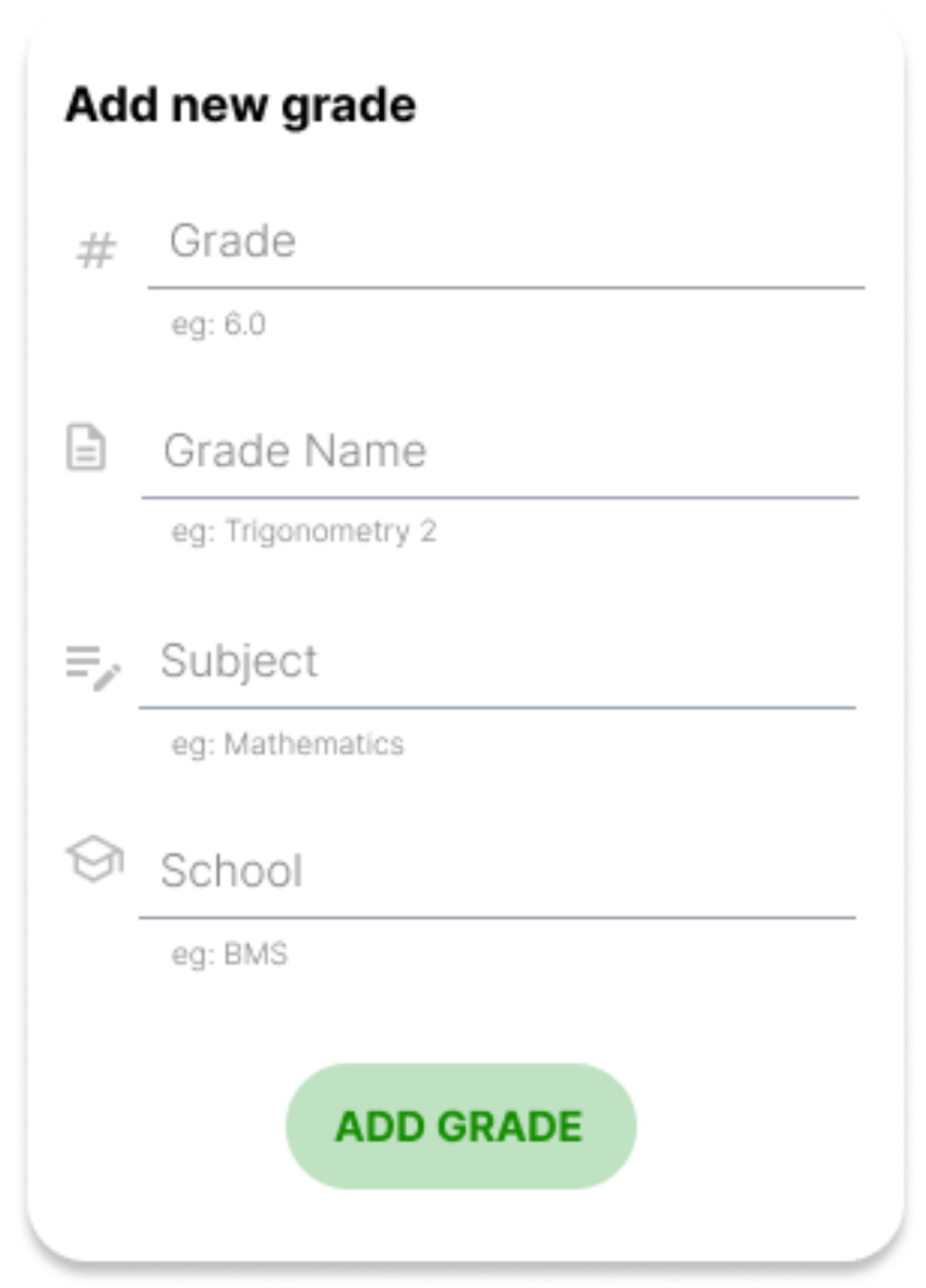
Grade: A score between 1 and 6, can include decimal places
Grade Name: The exam topic, e.g., "Trigonometry 2"
Subject: The subject where the exam took place, e.g., "Mathematics"
School: The school where this grade was obtained
Grade Editing Modal
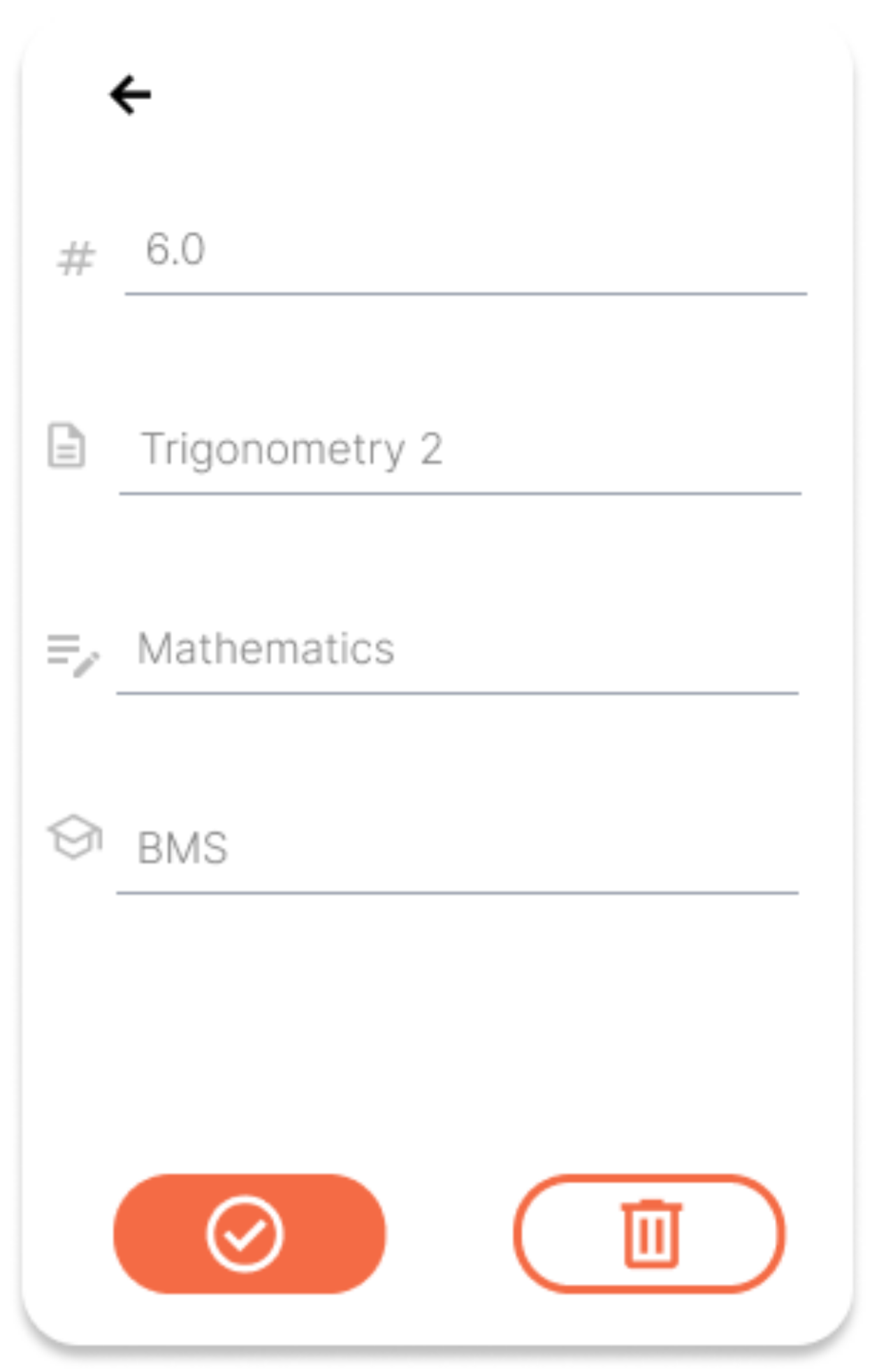
Users can edit recorded grades through this modal. The data of the grade to be edited is automatically filled in, and users can adjust any fields or delete the grade with the delete button.
Database Design
Entity Relationship Model (ERM)
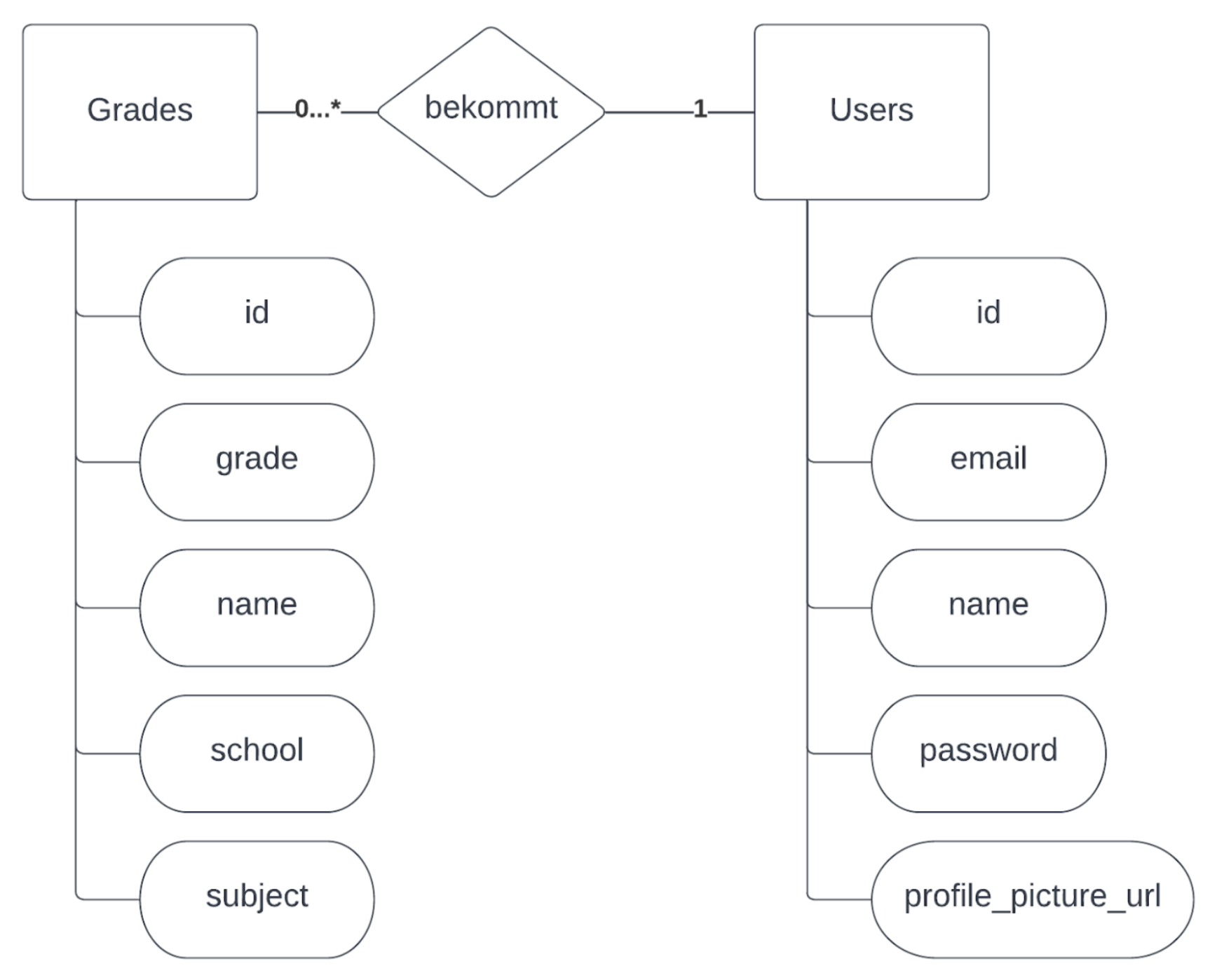
The ERM shows the relationship between Grades and Users, where multiple grades can belong to one user.
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD)
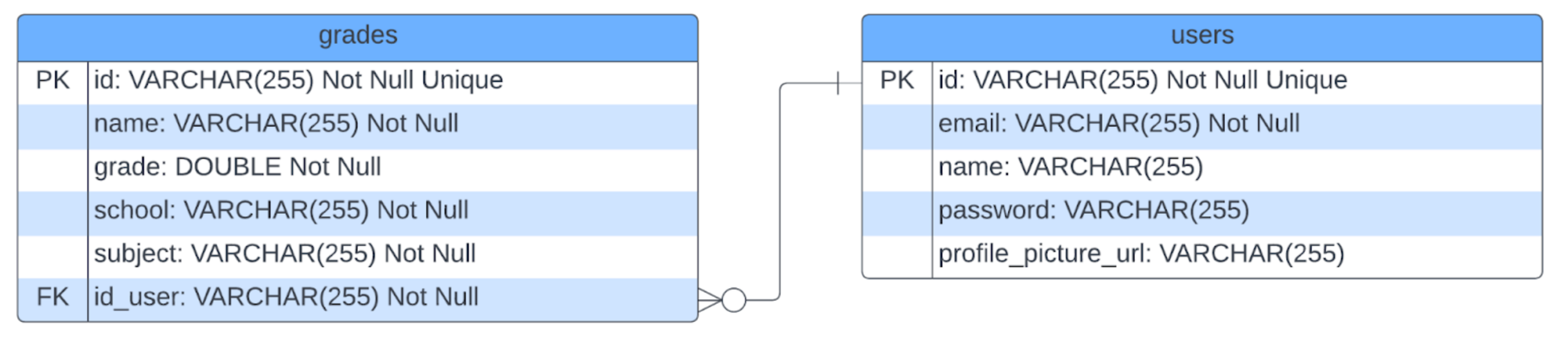
The ERD details the actual database schema with field types and constraints.
Database Schema Details
Grades Table
- PK: id (VARCHAR(255), Not Null, Unique)
- name (VARCHAR(255), Not Null)
- grade (DOUBLE, Not Null)
- school (VARCHAR(255), Not Null)
- subject (VARCHAR(255), Not Null)
- FK: id_user (VARCHAR(255), Not Null)
Users Table
- PK: id (VARCHAR(255), Not Null, Unique)
- email (VARCHAR(255), Not Null)
- name (VARCHAR(255))
- password (VARCHAR(255))
- profile_picture_url (VARCHAR(255))
UML Architecture
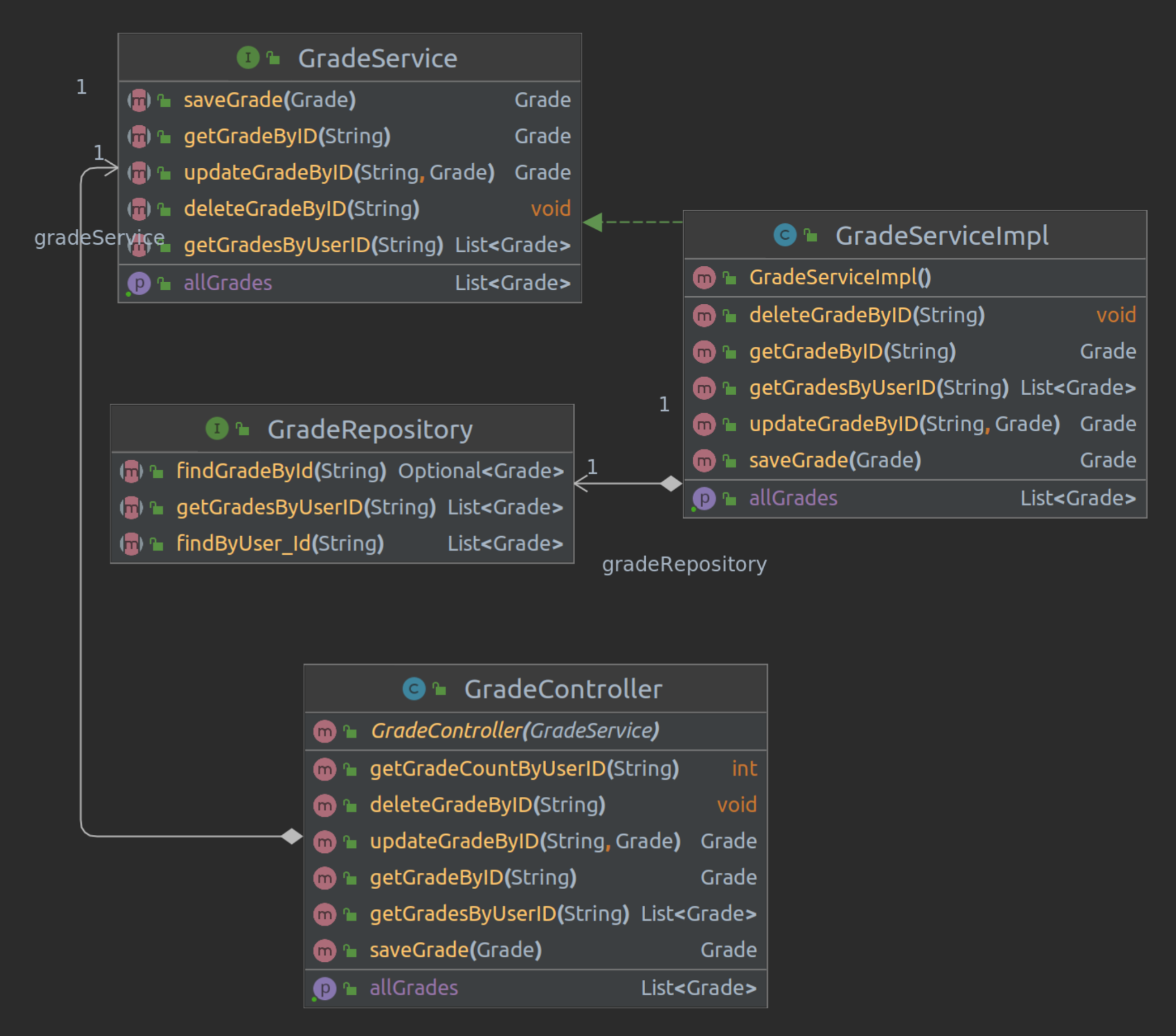
The UML diagrams show the typical structure of a Spring Boot application consisting of three main components: Repository, Controller, and Service. The Controller contains our API endpoints, the Repository enables JPA database access, and the Service implements the business logic executed when specific endpoints are called.
User Service Architecture
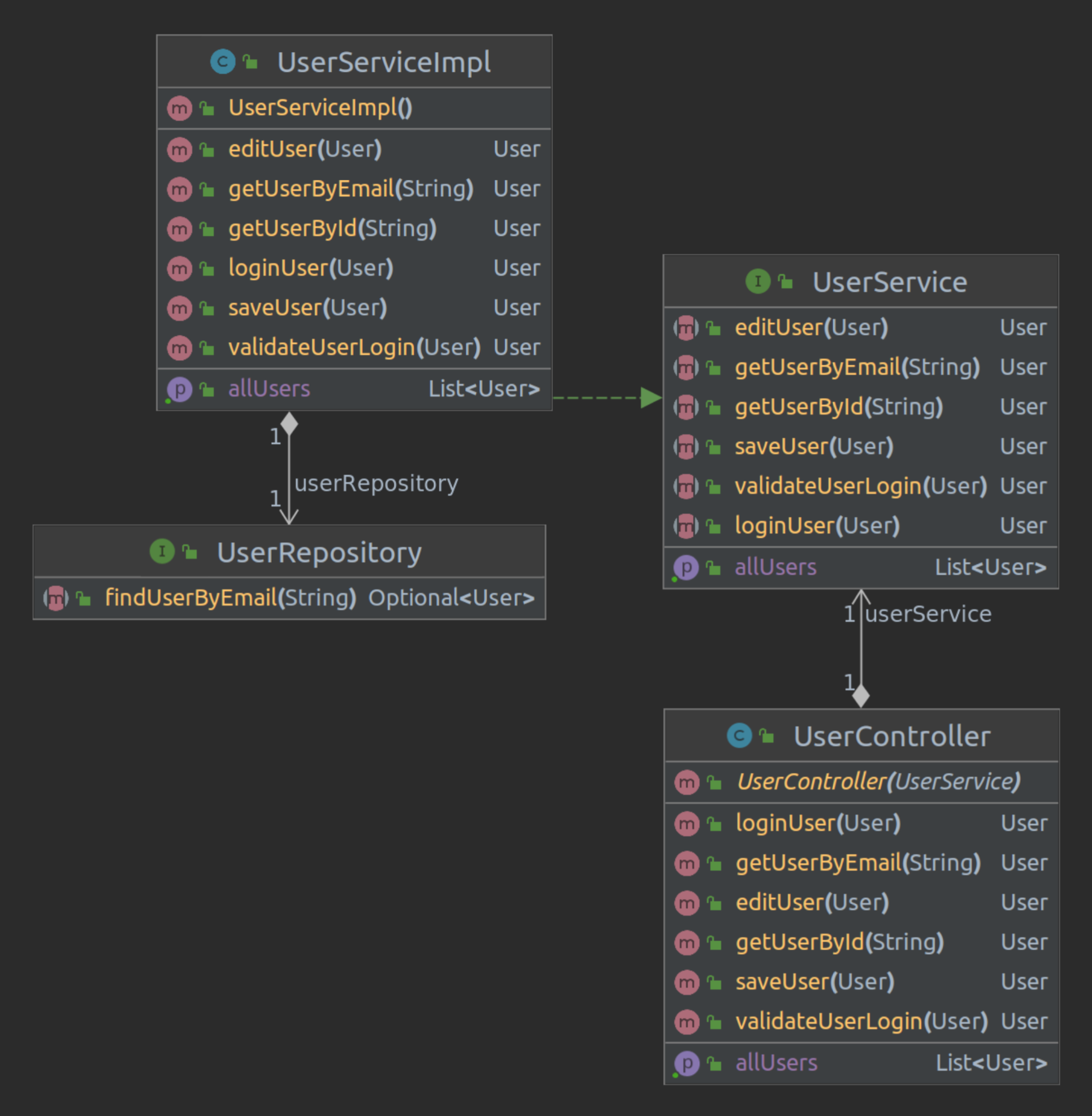
Grade Service Architecture
Testing & Quality Assurance
Testing Environment
Development Environment
- • Ubuntu 22.04
- • 17-inch display
- • IntelliJ IDEA (2022.1.2) & VS Code (1.67.1)
- • Android Emulator: Pixel 4 API 32
- • Java OpenJDK 18
Testing Environment
- • Pixel 4 API 32 (virtual device)
- • Expo Go (Version 2.24.4)
Test Cases
We conducted comprehensive testing covering all major functionality areas:
Navigation Testing
PASSEDTest Case #1 - Navigate between different pages
Action: Click "Grades" button in navbar
Expected: Navigation to "Grades Overview" page
Result: Successfully navigated to grades overview
Grade Listing
PASSEDTest Case #2 - Display all grades
Expected: All grades visible on screen
Result: All grades successfully displayed
Create New Grade
PASSEDTest Case #3 - Add new grade functionality
Actions: Navigate to add grade page → Fill in grade details → Submit
Result: Grade successfully created and saved
Edit Grade
PASSEDTest Case #4 - Edit existing grade
Actions: Click existing grade → Edit popup opens → Change grade from 6 to 4 → Confirm
Result: Grade successfully updated
Google Authentication
PASSEDTest Cases #6-7 - Google registration and login
Actions: Click Google button → Browser window opens → Login with Google credentials
Result: Successfully authenticated and navigated to main app
Theme Switching
PASSEDTest Case #9 - Toggle between light and dark mode
Actions: Navigate to settings → Click "Toggle Dark Mode" button
Result: Theme successfully switched
Testing Results Summary
All 9 test cases passed successfully, covering navigation, CRUD operations, authentication, and user interface functionality. The application demonstrates robust performance across all tested scenarios.
Project Outcomes & Learnings
Complete end-to-end application with modern architecture
Single codebase deployed across multiple platforms
Comprehensive testing ensuring reliability
This project successfully demonstrates the implementation of a modern full-stack mobile application using industry-standard technologies and best practices. The Grade Manager application showcases:
- • Modern Tech Stack: React Native frontend with Spring Boot backend and MariaDB database
- • Scalable Architecture: Clean separation of concerns with proper service layers and component structureco
- • User-Centered Design: Material Design 3 principles ensuring intuitive user experience
- • Robust Authentication: Google OAuth integration with persistent session management
- • Comprehensive Testing: Full test coverage across all major functionality areas
- • Effective Project Management: GitHub Projects integration for organized development workflow
The project demonstrates proficiency in full-stack development, from database design and backend API development to frontend mobile application creation and comprehensive testing practices.